近日,在新闻平台 HackerNews 上有个开发者颇为关注的 GitHub 项目,名叫 C++ Insights,特色就是:用编译器的眼睛看源码。为此,项目作者对其进行了详细介绍。
原文链接:https://github.com/andreasfertig/cppinsights
作者 | Andreas Fertig
翻译 | 郑丽媛
出品 | 程序人生(ID:coder_life)

C++ Insights 是什么?
C++ Insights 是一种基于 Clang 的工具,可进行源码到源码的转换,其目标是揭示通常情况下编译器在幕后为我们做的工作。它能帮我们看到编译器为了让代码正常运行而进行的一些神奇操作。
以下面这段代码为例:
class Base {
};
class Derived : public Base {
};
int main() {
Derived d;
Derived d2 = d;
d2 = d;
Base& b = d;
}
没有什么特别之处,当然也能编译。下面是编译器对它的看法:
class Base
{
public:
// inline constexpr Base() noexcept = default;
// inline constexpr Base(const Base &) noexcept = default;
// inline constexpr Base & operator=(const Base &) noexcept = default;
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
// inline constexpr Derived() noexcept = default;
// inline constexpr Derived(const Derived &) noexcept = default;
// inline constexpr Derived & operator=(const Derived &) noexcept = default;
};
int main()
{
Derived d;
Derived d2 = Derived(d);
d2.operator=(d);
Base & b = static_cast
(d);return 0;
}
你可以看到所有由编译器提供的特殊成员函数,以及从 Derived 向 Base 的向上转型。

为什么要做 C++ Insights?
2017 年,我开始研究 C++11、C++14 和 C++17 带来的一些新特性,如 lambda 表达式、基于范围的 for 循环和结构化绑定等。然而,所有这些研究以及我的一些培训和教学经历让我开始思考:如果我们能以编译器的视角来洞悉代码,那将会是怎样一番景象?当然,至少对于 Clang 来说,是有 AST(抽象语法树)转储功能的,我们可以用 Compiler Explorer 等工具查看编译器从 C++ 源代码片段生成的代码。不过,我们看到的是汇编程序,AST 和 Compiler Explorer 的输出并不是我写代码的语言,因此我对这些输出并不熟悉。另外,在教学生 C++ 时,如果跟他们展示 AST 并解释说这就是全部内容,我自己感觉也不太满意。
于是,我开始着手编写一个基于 Clang 的工具,可将基于范围的 for 循环转换为编译器内部版本。接着,我对结构化绑定和 lambda 也做了同样的处理。最终,我的工作超出了最初计划。
C++ Insights 这个工具显示了运算符的调用位置,以及编译器进行类型转换的情况,可以推断出 auto 或 decltype 背后的类型。我的目标是生成可编译的代码,然而,并非所有情况都能实现这一点。
例如,你可以看到 lambda、基于范围的 for 循环或 auto 的转换。当然,你也可以转换任何其他 C++ 代码段。
感兴趣的话,你可以亲自试试看。C++ Insights 在线使用网址:https://cppinsights.io/
不过,还有很多工作要做。我不敢说我做的一切都是正确的,目前我还在努力支持 C++20 等新标准的特性。请记住,C++ Insights 是基于 Clang 及其对 AST 的理解而建立的。

如何构建?
C++ Insights 可以在 Clang 源代码树内部或外部进行构建。
(1)在 Windows 上构建
已测试(支持的编译器)
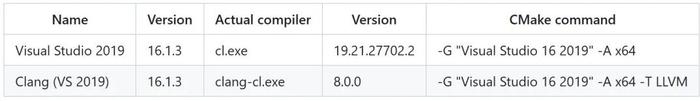
注意:仅支持在 LLVM 外部构建。不支持 x86,因为没有针对 x86 的 LLVM/Clang 库。
对于带有 VS 的 Clang:
前往 LLVM 下载页面;
从“Pre-Built Binaries”部分安装“Windows(64位)”;
安装程序会自动将 LLVM 工具集添加到你所有 Visual Studio 实例中。
从源代码构建和安装 Clang
需要有 Clang 库和 llvm-config.exe 来设置 CMake。
将 Clang/LLVM 库安装到(例如)C:\Programs\LLVM_local2。
注意:
安装路径中不能有空格;
最好不要使用 %Program Files%,否则需要管理员权限来安装文件。
git clone https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project.git
cd llvm-project
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS=clang ^
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=C:\Programs\LLVM_local2 ^
-G "Visual Studio 15 2017" ^
-A x64 ^
-Thost=x64 ^
..\llvm
cmake --build . --config Release --target install
你也可以在 Visual Studio 中打开 build/LLVM.sln 解决方案,然后在其中构建所有内容,而不是使用 cmake --build ... 命令。
构建 Insights
假设:
C++ Insights 源代码位于 C:\dev\cppinsights,并且
LLVM/Clang 已经构建并安装到 C:\Programs\LLVM_local2(参见上面的步骤)
cd C:\dev\cppinsights\
mkdir build
cd build
set path=%path%;C:\Programs\LLVM_local2\bin
cmake -G "Visual Studio 16 2019" -A x64 -T LLVM_v142 ..
cmake --build . --config Release --target insights
除了带“Visual Studio 16 2019”的 Clang,你还可以选择其他适合你的。具体可参见上面的 “已测试(支持的编译器)”,查看 CMake 命令列。另外,你也可以直接在 Visual Studio 中打开 build/cpp-insights.sln 文件进行构建,而不必通过命令行。
(2)在 Arch Linux 上构建
要使用 extra/clang 构建,请使用以下额外标记:
-DINSIGHTS_USE_SYSTEM_INCLUDES=off -DCLANG_LINK_CLANG_DYLIB=on -DLLVM_LINK_LLVM_DYLIB=on
extra/clang 和 extra/llvm 提供 /usr/lib/{libclangAST.so,libLLVM*.a,libLLVM.so},libclangAST.so 需要 libLLVM.so,如果链接的是 libLLVM*.a(而不是 libLLVM.so),就会发生冲突。
(3)在 Clang 外部构建
你需要在搜索路径中安装 Clang。
git clone https://github.com/andreasfertig/cppinsights.git
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -G"Ninja" ../cppinsights
ninja
生成的二进制文件(insights)可以在 build 文件夹中找到。
(4)在 Clang 内部构建
在 Clang 源代码树中 C++ Insights 最简单的方法,是使用 LLVM_EXTERNAL_PROJECTS 选项。
git clone https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project.git
git clone https://github.com/andreasfertig/cppinsights.git
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -G Ninja -D=CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DLLVM_EXTERNAL_PROJECTS=cppinsights -DLLVM_EXTERNAL_CPPINSIGHTS_SOURCE_DIR=
[INSIGHTS CMAKE OPTIONS] ../llvm-project/llvm
ninja
cmake 选项
cmake 可启用几个选项:
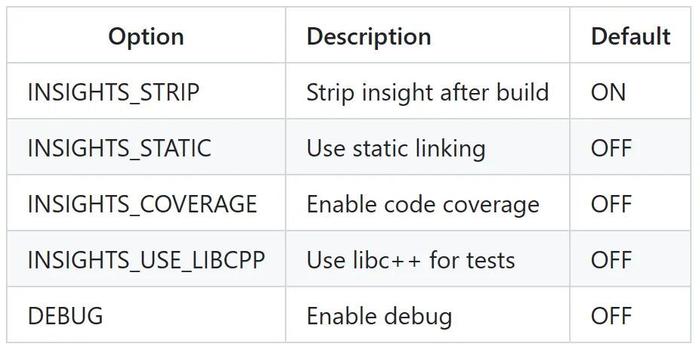
在 macOS 上构建 ARM
似乎最好在配置时提供架构:
cmake -DCMAKE_OSX_ARCHITECTURES=arm64 ../cppinsights

使用方法
使用 C++ Insights 非常简单:
insights
-- -std=c++17
当涉及到系统包含路径时,情况就变得复杂了。这些路径是二进制文件中的硬编码,似乎来自 C++ Insights 的编译器。要解决这个问题,可查看 scripts/getinclude.py,这个脚本会尝试从编译器中收集系统包含路径。如果没有选项,getinclude.py 将默认使用 g++,你也可以将其他编译器作为第一个参数传递。
下面是一个例子:
./scripts/getinclude.py
-isystem/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Toolchains/XcodeDefault.xctoolchain/usr/bin/../include/c++/v1 -isystem/usr/local/include -isystem/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Toolchains/XcodeDefault.xctoolchain/usr/bin/../lib/clang/7.3.0/include -isystem/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Toolchains/XcodeDefault.xctoolchain/usr/include -isystem/usr/include
该脚本可与 C++ Insights 一起使用:
insights
-- -std=c++17 `./scripts/getinclude.py`
自定义 GCC 安装
如果你用的是自定义版本的 GCC 编译器,例如 gcc-11.2.0,且未安装在编译器的默认系统路径中,那么在构建后,Clang 将无法找到正确的 libstdc++ 路径(即 GCC 的标准模板库)。如果遇到这种情况,你可以用“--gcc-toolchain=/path/GCC-1x.x.x/installed/path”来告诉 Clang/C++ Insights STL 的位置:
./cppinsights Insights.cpp -- --gcc-toolchain=${GCC_11_2_0_INSTALL_PATH} -std=c++20
这里的“${GCC_11_2_0_INSTALL_PATH}”是你定制构建的 GCC 安装目录。
随时可用的 Docker 容器
GitHub 上还有另一个项目,可以在其中设置一个装有最新 C++ Insights 版本的 docker 容器:C++ Insights - Docker(https://github.com/andreasfertig/cppinsights-docker)
C++ Insights @ Vim
Vim 插件可在此处下载:https://github.com/Freed-Wu/cppinsights.vim
C++ Insights @ VSCode
Visual Studio Code 的扩展可在此处找到:https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=devtbi.vscode-cppinsights
C++ Insights @ brew
至少在 macOS 上,你可通过 Homebrew 安装 C++ Insights,这要归功于这个公式:
brew install cppinsights

兼容性
我的目标是,能够与最新版本的 Clang 或者至少前一个版本保持兼容,在线网站尽量与 Clang 的最新版本保持一致。然而,由于某些问题(比如为 Windows 构建 Clang),网站的版本经常会延迟几个月。
更多详细介绍,可参看 C++ Insights 项目 GitHub 地址:https://github.com/andreasfertig/cppinsights

4000520066 欢迎批评指正
All Rights Reserved 新浪公司 版权所有

